Steps in the Accounting Cycle - Example
Here we discuss about steps in the Accounting Process.
Accounting Cycle is the basic of the Accounting. The whole system
of accounting processes are operated throughout the Accounting period is called
Accounting Cycle. Every Step has its great importance. We can not ignore any
one of these. There are following steps / stages in the Accounting Cycle and we can say that the Accounting Process begins with the following Accounting Cycle Steps:
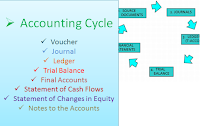
Accounting Cycle Order
1.
Voucher (Source Document)
2.
Journal (Recording)
3.
Ledger
4.
Trial Balance
5. Final Accounts (Income Statement and Balance Sheet)
6.
Cash Flow Statements
7.
Statement of Changes in Equity
8.
Notes to the accounts
1)
Voucher (source Document)
Voucher means any written evidence in support of transactions. For
example, when we sold goods to Mr. A, then we give him / her a Sale receipt for
selling goods. This receipt is called Voucher.
2)
Journal (Recording)
For Journal, Please you can referred to Journal Format for better understanding about this topic.
Recording of transactions in the books of account after verifying from the voucher or source document. For example, recording sales transactions in the Sales book after verifying from voucher receipt of the sales.
3)
Ledger
For Ledger, Please read this Ledger
After recording transactions in the journal, all theses are posted to their concerned accounts. Business Account Ledger is called the king of books of accounts.
For example, all the transactions of Sales to any person either made in cash or credit are recorded in the ledger.
After posting the transaction to concerned accounts, Accounting Trial Balance
is prepared to show the Arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts.
Is the Total of Debit Balance equal to the Total of Credit Balance means that accounts are prepared accurately?
The answer is no, because, merely the total equality of both debit
balance and credit balance does not give us guarantee that there are no errors
or fraud in the books of accounts, so this is the limitation of Trial Balance.
For this Rectification of errors and frauds are made.
5)
Final Accounts
Final Accounts are prepared after the end of accounting period.
Final Accounts include the Income Statement (Statement of Comprehensive Income)
and Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position).
i. Income Statement
Income Statement
shows us financial performance (Net Income) of the business.
ii. Balance Sheet
Balance Sheet shows
us financial position of the business.
6)
Cash Flows Statements
Cash Flows
Statement shows us Cash inflow and Cash outflow of the business. It shows the
Liquidity position of the company.
Note: You may also be interested in Statement of Cash Flows Example
Note: You may also be interested in Statement of Cash Flows Example
There are three
components of this statement:
i. Operating Activities
Operating activities include those Cash Transactions that are
important for the operations of the business. Revenues and Expenses and Working
Capital are example.
ii. Investing Activities
Cash involves
in investing related transaction, Purchase of Fixed Assets, Disposal of Fixed
Assets and Cash investments.
iii. Financial Activities
Cash Flows
involve the financial related activities like Cash received from issuance of
capital, Cash Dividend, Repayment of debts.
Changes in
Equity are recorded in this account. Retained Earnings, Share Capital, General
Reserves, are transferred to this statement.
These notes are
provided for the necessary explanation of the accounting transaction For
example, we provide the detail of contingent liability (that depends on the
happening of certain event) in Notes to the accounts section.
So, hopefully now you
can understand the above mentioned steps in the Accounting Cycle that are explained
through example.
Comments